New mosquito-borne virus spreads in Latin America
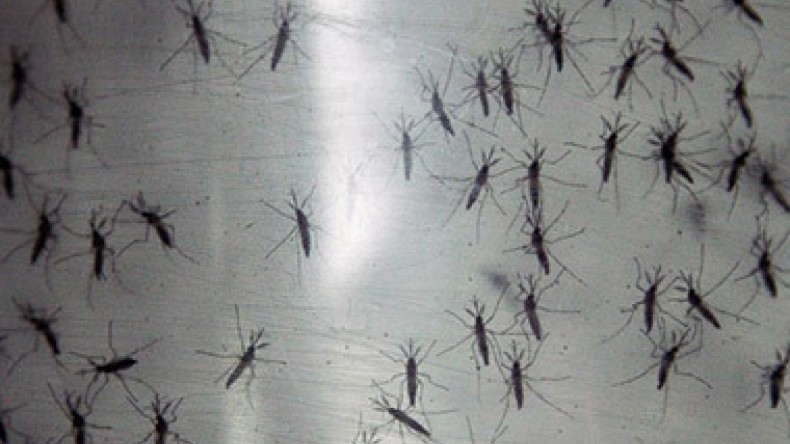
An excruciating mosquito-borne illness that arrived less than a year ago in the Americas is raging across the region, leaping from the Caribbean to the Central and South American mainland, and infecting more than 1 million people. Some cases have already emerged in the United States, The Associated Press reported.
While the disease, called chikungunya, is usually not fatal, the epidemic has overwhelmed hospitals, cut economic productivity and caused its sufferers days of pain and misery. And the count of victims is soaring.
In El Salvador, health officials report nearly 30,000 suspected cases, up from 2,300 at the beginning of August, and hospitals are filled with people with the telltale signs of the illness, including joint pain so severe it can be hard to walk.
"The pain is unbelievable," said Catalino Castillo, a 39-year-old seeking treatment at a San Salvador hospital. "It's been 10 days and it won't let up."
Venezuelan officials reported at least 1,700 cases as of Friday, and the number is expected to rise. Neighboring Colombia has around 4,800 cases but the health ministry projects there will be nearly 700,000 by early 2015. Brazil has now recorded its first locally transmitted cases, which are distinct from those involving people who contracted the virus while traveling in an infected area.
Hardest hit has been the Dominican Republic, with half the cases reported in the Americas. According to the Pan American Health Organization, chikungunya has spread to at least two dozen countries and territories across the Western Hemisphere since the first case was registered in French St. Martin in late 2013.
There have been a few locally transmitted cases in the U.S., all in Florida, and it has the potential to spread farther, experts say, but Central and South America are particularly vulnerable. The chief factors are the prevalence of the main vector for the virus, the aedes aegypti mosquito, and the lack of immunity in a population that hasn't been hit with chikungunya in modern medical history, said Scott C. Weaver, director of the Institute for Human Infections and Immunity at the University of Texas Medical Branch.
Newsfeed
Videos