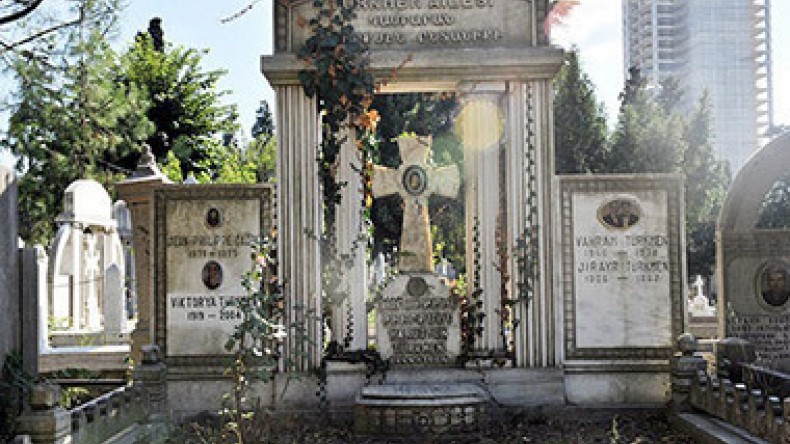
Historic cemetery returned to Armenians in Istanbul
The Armenian community of Turkey has won a legal battle for the ownership of a historic cemetery in Istanbul in the latest success story for the return of properties seized from minorities in the wake of legal amendments, the Daily Sabah reports, according to Asbarez.
The Turkish Prime Ministry’s Directorate General of Foundations, which oversees properties belonging to religious and ethnic minorities, has handed over the title deed for an ancient Armenian cemetery in Istanbul’s central Şişli district to an Armenian church organization.
Following new laws requiring the return of properties to their rightful owners, Beyoğlu Üç Horan (Yerrortutyun or Trinity) Church Foundation had applied to the Directorate in 2011 for the ownership of the cemetery. After four years and a settlement of legal matters, the Directorate granted ownership to the foundation for the cemetery, which covers some 41,950 square meters in the heart of Istanbul.
The cemetery’s history dates back to the 19th century in which a Sultan’s decree ordered its handover to the Armenian community. In the 1930s, its ownership was transferred to the Istanbul Municipality. Yet, Armenian families were allowed to bury their deceased next of kin in the cemetery even though they had no official deeds for the plots.
Among the cemetery’s notable occupants are Arman Manukyan, a notable professor of economy from Boğaziçi University, opera singer Toto Karaca, composer Onno Tunç, Armenian patriarchs, and Armenian lawmaker Berç Keresteciyan Türker, who is known for his contributions to the Turkish War of Independence.
The place is the latest property that the Armenian community has obtained back after their confiscation by the state. In 2012, the Directorate General of Foundations had returned the title deed of the Armenian Catholic Cemetery in Şişli to the community and a valuable plot in Zeytinburnu district to Yedikule Surp Pergich Hospital Foundation.
Foundations set up by non-Muslim minorities were granted the right to acquire properties in 1912 but a new law in 1935 ordered them to declare the properties they owned and register their title deeds. In 1936, a list of entire properties owned by minorities was handed to the Directorate General of Foundations and minorities were prevented from acquiring any property other than those in the list, thanks to an unofficial ban that was viewed as the state’s hostility towards minorities who were treated as “second-class” citizens. In 1976, the Turkish Supreme Court of Appeals had effectively enforced the ban and also ordered the return of properties minorities had acquired until that year. Soon, countless plots and buildings, especially in upscale districts of Istanbul, were handed to the Treasury after their seizure from Greek and Armenian communities.
Markar Esayan, a columnist for Daily Sabah, says minorities have suffered from “illegal policies” of the state-run foundations authority that exploited legal loopholes. “Until [2008], they suffered at the hands of fascistic measures,” he says, referring to the year that an amendment in the relevant laws “helped the state to repair its past mistakes.”
“Laws in the past dealt a blow to the self-sustainability of the churches whose survival solely depended on schools, hospitals and other sources of revenues,” Esayan says. He noted that a series of decrees helped minorities to regain their rights in terms of return of properties. “Currently, properties returned constitute 10 percent of the total properties supposed to be returned. Nevertheless, it is a very important, democratic step that the state stopped seeing minorities as enemies,” Esayan says. He said that minorities complain of several technical shortcomings in laws regarding church foundations that sometimes complicate the procedure of returning the properties. “The rate of returns is not sufficient. Yet, what matters more now is a change in the mindset, a very radical change (in the view of minorities by the state),” he says.
Associate Professor Toros Alcan, chairman of Armenian community’s Surp Haç Tibrevank Foundation and board member of Directorate General of Foundations, says the return of properties was “what the minorities yearned for decades.” “I can safely say on behalf of minorities that we are very happy with decisions to return the properties,” Alcan says. He said what then prime minister and incumbent president Recep Tayyip Erdoğan once said, “It is not a blessing by the state for minorities but rather a resumption of their rights.”
Newsfeed
Videos