Legend about beautiful Shahandukht and church she founded – scientific publication of Russian Empire
In the 13th issue for the year 1892 of the project “The Collection of Materials to Describe the Terrain and Tribes in the Caucasus,” the inspector of Sar school, N. Grigorov, published an essay dedicated to the ancient Armenian village Tatev, the monuments in its surroundings, and the legends about it.
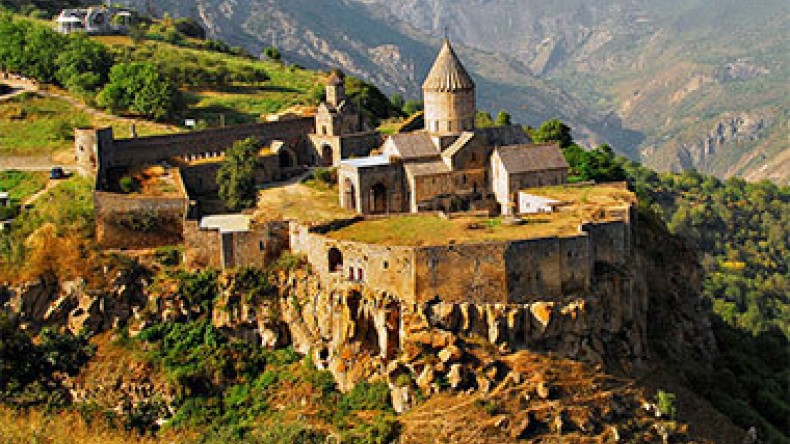
The village Tatev takes its name from Tatev Monastery situated not far from it. The name derives from the Armenian words “Տա-Թեւ,” which are translated as “give wings.”
There is an Armenian legend about the origin of that name. According to it, an experienced bricklayer successfully finished the construction of Tatev Monastery and standing on a high wall asked the workers to bring him two small boards. Taking them in his hands, he kissed them and said, “Հոգին Սուրբ տա թեւ” (“May the Holy Spirit give wings”). “The moment he pronounced these words, wings grew on him and he flew away. In vain did the workers and gathered Christians try to find the bricklayer in the surroundings of Tatev. The local Christians did not know how to dismantle the enormous scaffold erected in the temple for construction but they heard that the bricklayer, constructor of the monastery lived in Constantinople. So they sent an envoy asking him to come back and complete the construction of the temple. Despite the envoy’s persistent requests, the bricklayer did not return to Tatev but opened him the secret how to dismantle the scaffold,” the legend says.
The village Tatev is situated in the center of Zangezur uyezd, not far from the city Gerusi (Goris. – ed.) 105 versts (about 111km) from Shushi. Tatev’s picturesque surroundings are rich in vegetation and the villages are surrounded by pastures reaching to Tatev Monastery and the splendid forests, which covered the neighboring mountains and went with terraces down to the gorge of the river. Thanks to the beautiful scenes, Tatev was long used by Syunik governors as residence.
As for the ethnic composition of the population in Tatev and surrounding villages, the author notes that the whole population was exclusively Armenian of Armenian Gregorian faith. “With the exception of the three families of noble Orbelians and several families of spiritual rank, the population is of tax-paying class,” the author writes.
“The people in Tatev are very peaceful, kind and unusually thrifty. There is even a saying about their love for work, ‘He who does not do his work in time, cannot be Tatevian’,” Grigorov cites.
Further, he presents the sights and religious structures in the surroundings of Tatev. In particular, he writes about the church Shahandukht (Շահանդուխտ), a dilapidated church at the bottom of a deep valley. It was built by the maid Shahandukht, whose relics were later buried there. The valley also bears her name – Shahandukht gorge (“Շահանդուխտի ձոր”).
Orbelian recounts a legend, which says Shahandukht, the daughter of the great Aghwanian knight Trdat, had rare beauty. Hearing about her, the Persian khans started to look for an occasion to kidnap her. Meanwhile, the Knight of Syunik proposed to her, but when she was on her way to her fiancé’s home, Persian troops sent by the khan attacked them trying to seize her. When the fiancée and her suite reached the cliff, a bloody fight unfolded between the Armenians and the Persians, and many people were killed from both sides. Being aware of the reason of the people’s death, the devout girl turned her horse, placed a cross on herself, and asking for St. Theotokos and St. Hripsimeh’s help threw herself off the cliff into the dreadful abyss. The Providence preserved Shahandukht, and she landed safe and sound with her horse. When the sanguine fight was over, the fiancé and his companions found her where she had thrown herself. However, despite her parents and fiancé’s persistent requests to get married, she renounced the worldly vanities and made a nun,” the legend says.
Soon Shahandukht became widely renowned in the surroundings and lay sisters started to come to her. With their help, she built a small church under the rock. Then Shahandukht invited the Bishop of Tatev and handed him all the valuables her parents had given her as dowry. She asked the bishop to give half of those things to the poor, and make the rest of them the property of the monastery.
Shahandukht passed away 30 years after taking the veil. When the bishop of Tatev Monastery learnt about her decease, he came and buried the holy maid’s relics inside the church she had built.
To be continued.
“The Collection of Materials to Describe the Terrain and Tribes in the Caucasus” is a large-scale publication of narrative sources carried out by the management of the Caucasus Educational Okrug in 1881-1908. It includes researches and description of the history, life, and ethnographic characteristics of the peoples inhabiting the Caucasus region of the Russian Empire.
Related:
Scientific publication recounts historical data about C15th Armenian village Kusapat in Artsakh
Scientific edition of Russian Empire: Nakhijevan was prominent Armenian city founded in C16 BC
19th century scientific edition of Russian Empire compiled historical data about ancient Erivan
Newsfeed
Videos