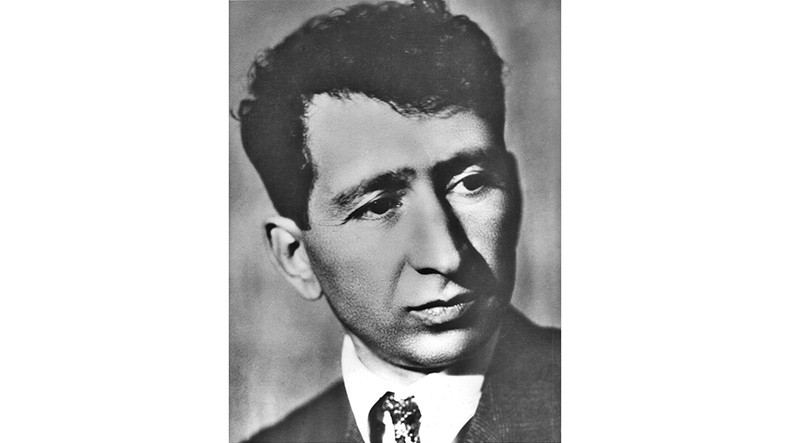

Today marks 121st birth anniv. of renowned Armenian poet Yeghishe Charents
March 13 marks the 121st birth anniversary of prominent Armenian poet Yeghishe Charents.
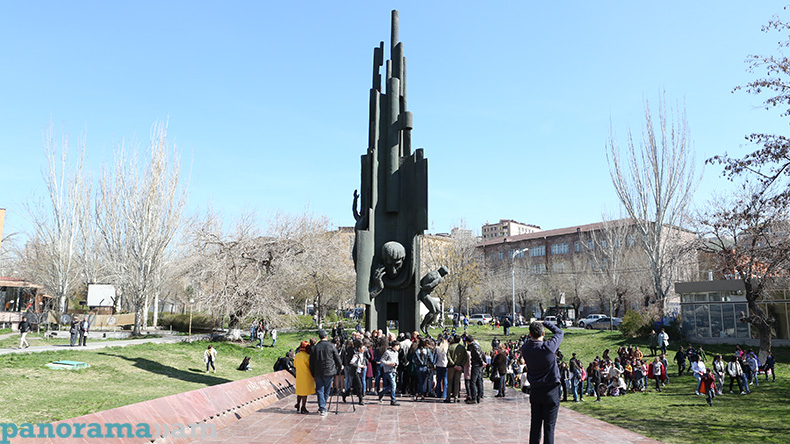
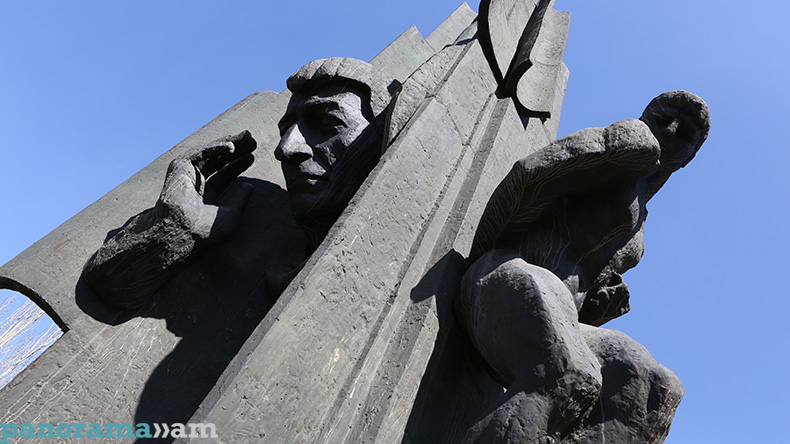
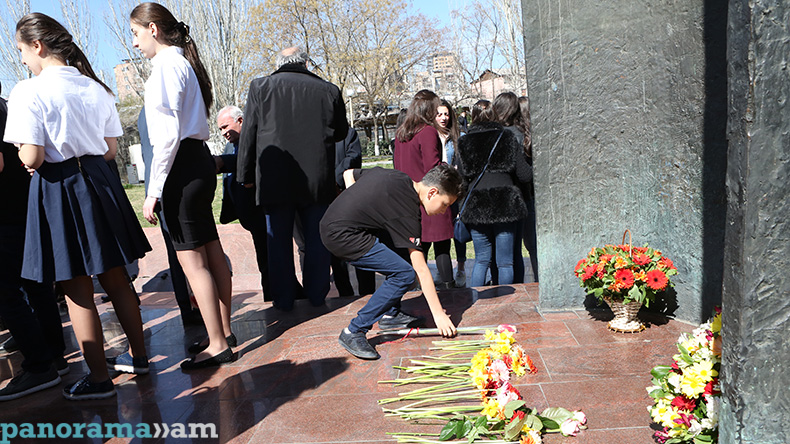
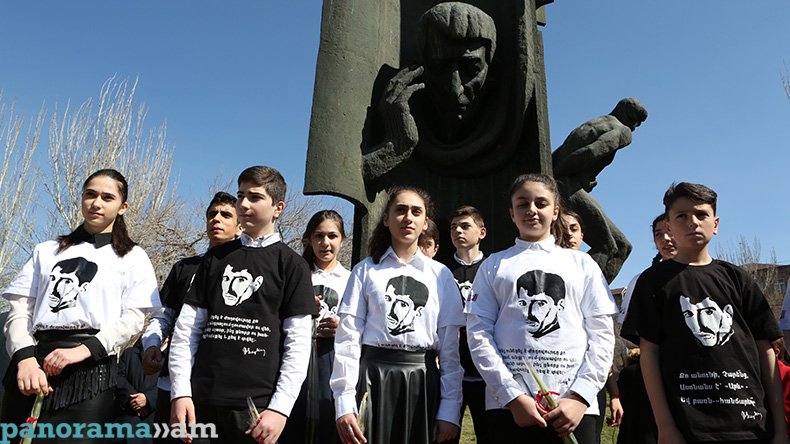
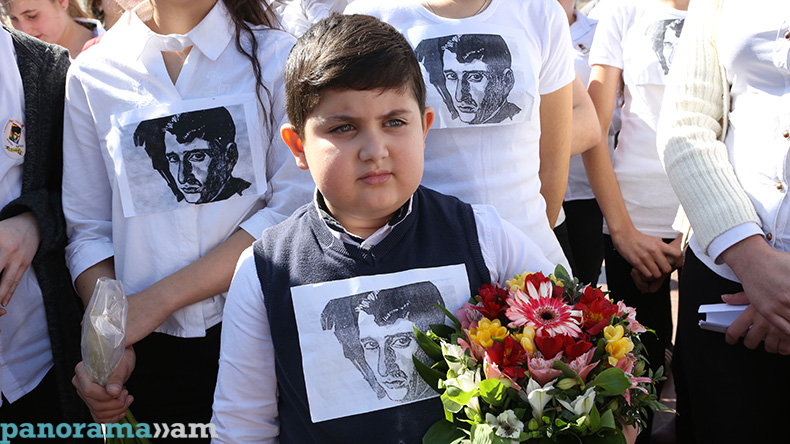
Events dedicated to the great poet’s birthday kicked off today at Yeghishe Charents Monument, with the lovers of the renowned poet’s works gathering around the monument to pay tribute to his memory.
Yeghishe Charents (Yeghishe Soghomonyan) was born in Kars (then a part of the Russian Empire) in 1897 to a family engaged in rug trade.
He first attended an Armenian, but later transferred to a Russian technical secondary school in Kars from 1908 to 1912. In 1912, he had his first poem published in the Armenian periodical Patani (Tiflis).
Amid the upheavals of the First World War and the Armenian Genocide in the Ottoman Empire, he volunteered to fight in a detachment in 1915 for the Caucasian Front. Sent to Van in 1915, Charents was a witness to the destruction that the Turkish garrison had laid upon the Armenian population, leaving indelible memories that would later be read in his poems. He left the front one year later, attending school at the Shanyavski People's University in Moscow. The horrors of the war and genocide had scarred Charents and he became a fervent supporter of the Bolsheviks, seeing them as the one true hope to saving Armenia.
Charents joined the Red Army and fought during the Russian Civil War as a rank and file soldier in Russia and the Caucasus. In 1919, he returned to Armenia and took part in revolutionary activities there. A year later, he began work at the Ministry of Education as the director of the Art Department. Charents would also once again take up arms, this time against his fellow Armenians, as a rebellion took place against Soviet rule in February 1921. Then, Charents published his satirical novel, Land of Nairi (Yerkir Nairi), which became a great success and twice published in Russian in Moscow during the life of poet.
In 1924-1925 Charents went on a seven-month trip abroad, visiting Turkey, Italy (where he met Avetik Isahakyan), France, and Germany. When Charents returned, he founded a union of writers, November, and worked for the state publishing house from 1928 to 1935.
In 1930 Charents's book, "Epic Dawn", which consisted of poems he wrote in 1927-30, was published in Yerevan. It was dedicated to his first wife Arpenik.
His last collection of poems, "The Book of The Way", was printed in 1933, but its distribution was delayed by the Soviet government until 1934, when it was reissued with some revisions. In this book the authors lays out the panorama of Armenian history and reviews it part-by-part. William Saroyan met him in 1934 in Moscow and thereafter described him as a courtly, brilliant man who was desperately sad.
Excepting few poems in journals, Charents could publish nothing after 1934 (at the same time, in December 1935 Stalin asked an Armenian delegation how Charents is).
In July 1936, when Soviet Armenian leader Aghasi Khanjian was killed, Charents wrote a series of seven sonnets. After Komitas's death he wrote one of his last great works, "Requiem Æternam in Memory of Komitas" (1936).
Actress Arus Voskanyan told about her last visit to Charents: "He looked fragile but noble. He took some morphine and then read some Komitas. When I reached over to kiss his hand he was startled". He became a morphine addict under the pressure of the campaign against him and because he was suffering from colic, caused by a kidney stone. The hypodermic needle Charents used for his habit is on exhibit in his museum in Yerevan.
A victim of Stalinism, he was charged for "counterrevolutionary and nationalist activity" and imprisoned during the 1937 Great Purge. He died in prison hospital. All his books were also banned. Charent's younger friend, Regina Ghazaryan buried and saved many manuscripts of the Armenian poet. Charents was rehabilitated in 1954 after Stalin's death.
Charent's works were translated by Valeri Bryusov, Anna Akhmatova, Boris Pasternak, Arseny Tarkovsky, Louis Aragon, Marzbed Margossian, Diana Der Hovanessian, and others. His home at 17 Mashtots Avenue in Yerevan was turned into a museum in 1975. The Armenian city Charentsavan was named after him.




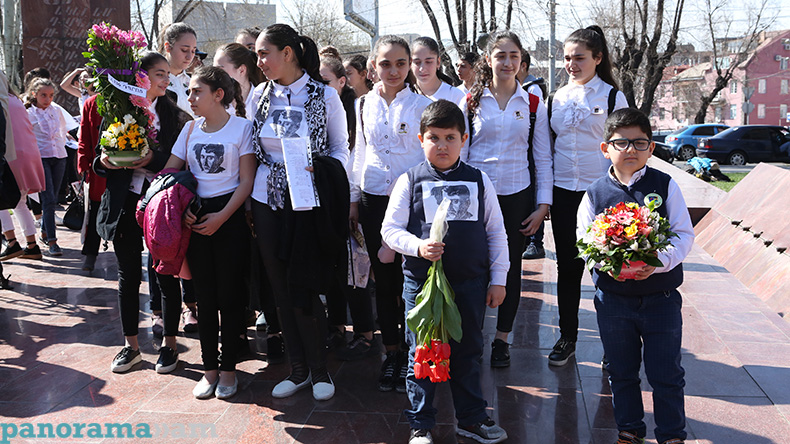



Newsfeed
Videos






























